Subtitle
Proton Radiotherapy for Management of Medulloblastoma: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes
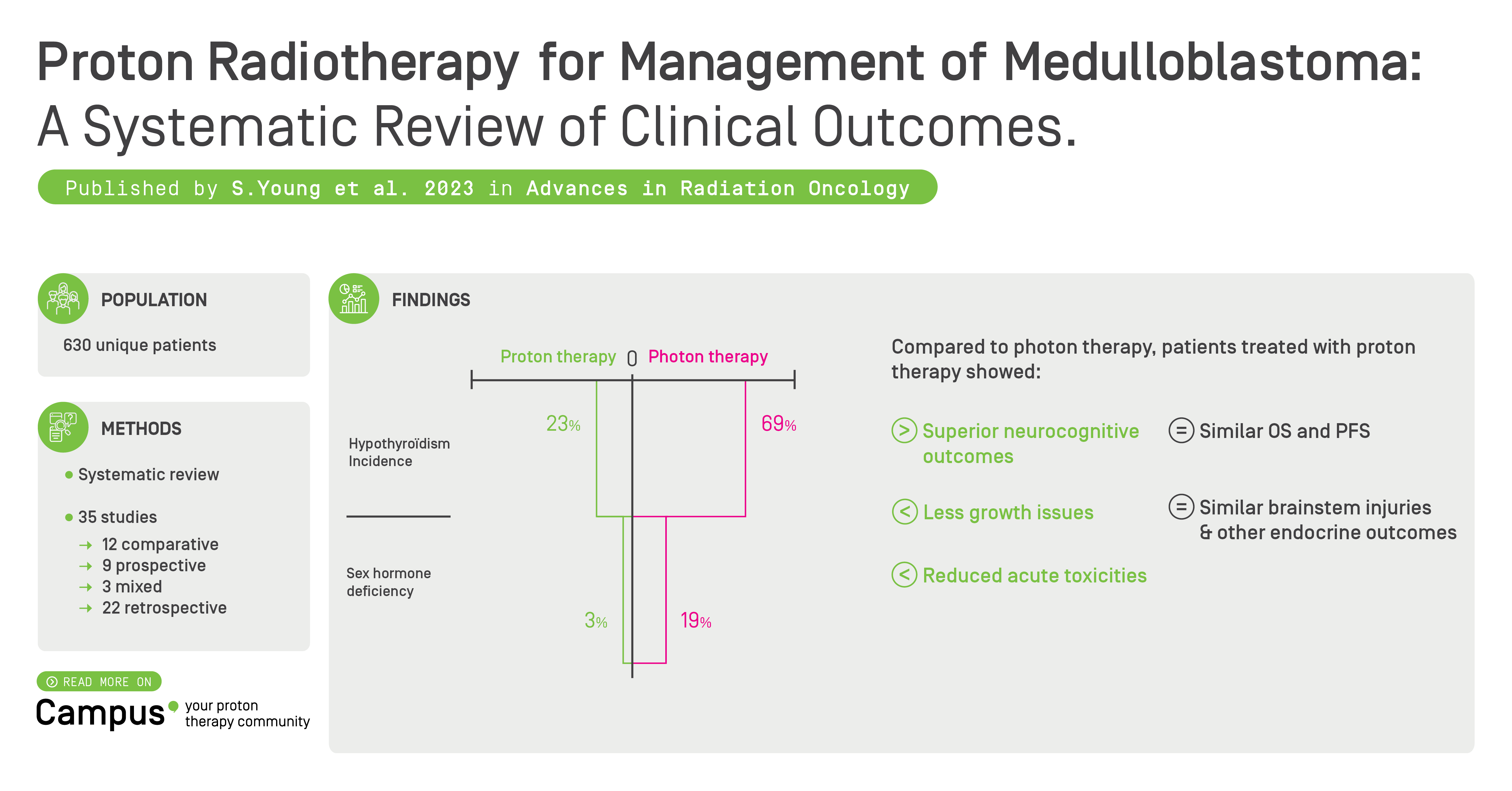
This comprehensive review found moderate grade clinical evidence supporting proton-CSI as the preferred delivery technique for both children and adults with medulloblastoma (MB). Thirty-five original studies (representing an estimated 630-654 unique patients) that reported clinical outcomes were included for analysis in this review. The majority of studies (n = 32) were from the United States, with 17 studies from researchers affiliate with Massachusetts General Hospital. There were 12 comparative, 9 prospective, 3 mixed, and 22 retrospective studies, but randomized study. This review reported that well-designed comparative cohort studies with adequate follow-up have demonstrated superior neurocognitive outcomes, lower incidence of hypothyroidism (23% vs 69%), sex hormone deficiency (3% vs 19%), greater heights, and reduced acute toxicities in patients treated with protons compared to photons. OS (up to 10 years), PFS (up to 10 years), brainstem injury, and other endocrine outcomes were similar to those reported for photon radiation.